Interesting Facts For Flat Feet and Bunions
Flat feet and bunions are two common foot problems that can affect mobility and comfort. Many people wonder if there is a connection between these two conditions. Flat feet can increase the risk of developing bunions, as the structural issues in the foot can lead to uneven pressure on the joints. This relationship is important to understand for those who experience foot pain or discomfort.
People with flat feet often have arches that collapse, which can cause their feet to roll inward excessively. This can create additional strain on the big toe joint, leading to the formation of bunions over time. It is crucial to address both conditions early to prevent further complications.
Awareness of flat feet and their potential impact on bunions can motivate individuals to seek preventive measures or treatment options. With the right information and care, managing these foot conditions becomes more achievable.
Understanding Flat Feet
Flat feet, also known as pes planus, is a condition where the arches of the feet are flattened. This can lead to various issues, including discomfort and misalignment. The following sections will discuss the definition and prevalence of flat feet, the anatomy involved, and the common causes of this condition.
Definition and Prevalence
Flat feet occur when the arch of the foot collapses, causing the entire foot to touch the ground. This condition can be present from birth or develop over time. It is estimated that around 20-30% of the population has flat feet to some degree. Some people might experience no symptoms, while others may suffer from pain in the feet, ankles, or legs. The condition can also be more common in certain groups, including athletes and individuals over 50.
Anatomy of Flat Feet
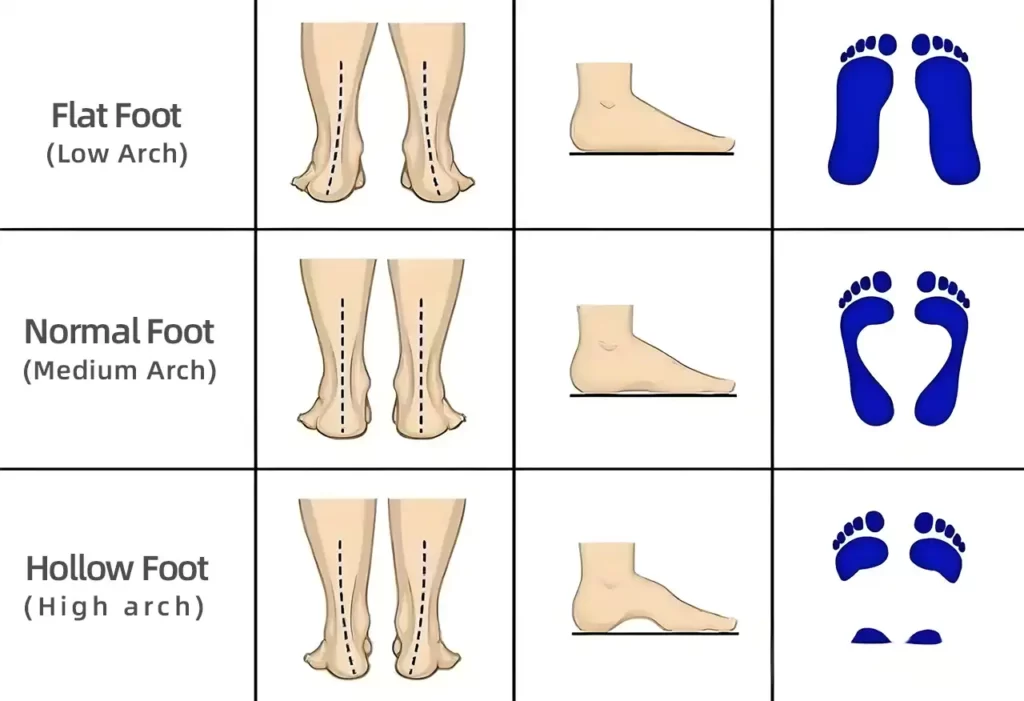
The foot consists of several bones, muscles, and tendons that work together to support the body. The arch is formed by the tarsal and metatarsal bones, along with ligaments and muscles. In a normal foot, the arch helps to absorb shock and distribute weight evenly when walking. In flat feet, the arch is either not developed or collapses, leading to uneven weight distribution. This can cause issues in other parts of the body, such as the knees and hips, due to altered biomechanics.
Causes of Flat Feet
Flat feet can result from various factors, including genetics, age, and lifestyle. Some people inherit the tendency to have flat feet from their parents. As individuals age, the ligaments and tendons can weaken, leading to a loss of arch support. Other contributing factors may include obesity, which adds extra pressure on the feet, and certain medical conditions, such as arthritis or diabetes. Overuse, particularly in athletes, can also lead to flat feet due to muscle fatigue and inflammation.
Overview of Bunions

Bunions are bony bumps that form at the base of the big toe. They can cause pain and limit mobility if left untreated. Understanding the identification, risk factors, and formation process of bunions helps in recognizing and managing this condition effectively.
Identification and Symptoms
A bunion appears as a protruding bump on the inside of the big toe joint. It can cause redness and swelling in the area. Symptoms may include:
- Pain: Discomfort can arise from wearing tight shoes.
- Inflammation: The skin over the bunion may become red and sore.
- Limited movement: It can be painful to move the big toe.
- Bunionettes: Smaller bunions may develop on the joint of the little toe.
Recognizing these symptoms early can help in seeking appropriate treatment.
Risk Factors for Bunions
Several factors increase the likelihood of developing bunions. These include:
- Footwear: Wearing tight or narrow shoes can worsen bunion formation.
- Genetics: A family history of bunions can enhance the risk.
- Foot structure: Conditions like flat feet or high arches can contribute to bunion development.
- Medical conditions: Arthritis and other conditions affecting the joints may also lead to bunions.
Being aware of these risk factors assists individuals in taking preventive measures.
Bunion Formation Process
Bunions form when the big toe is pushed out of alignment. This misalignment can gradually lead to the bony bump. Contributing steps in this process include:
- Foot structure: Flat feet often cause the big toe to turn inward.
- Pressure: Repeated stress from footwear can exacerbate the issue.
- Inflammation: Joint inflammation from conditions like arthritis can play a role.
- Progression: Over time, the misalignment worsens, forming a visible bump.
Understanding this formation can help in preventing bunion progression and managing symptoms early.
Link Between Flat Feet and Bunions
Flat feet, or fallen arches, can play a significant role in the development of bunions. When feet are flat, they often roll inward, a condition known as overpronation. This movement places extra pressure on the big toe joint, which can lead to bunion formation.
Key Factors of the Link:
- Inward Rolling: Flat feet contribute to excessive inward rolling, causing the big toe to push against adjacent toes.
- Pressure on Joints: The abnormal pressure on the big toe joint can trigger bunions.
- Foot Shape: Certain foot shapes, especially those with low arches, are more prone to bunions.
Individuals with flat feet often wear shoes that do not provide adequate support. Narrow or ill-fitting shoes can make the situation worse. They can squeeze the toes and increase the risk of bunion growth.
Researchers indicate that genetics also plays a role. Bunions often run in families, meaning those with certain foot types may be more likely to develop them.
Proper footwear and custom orthotics can help manage symptoms. These can support the arch and reduce pressure on the big toe joint. Understanding this link can help in taking preventive measures against bunions.
Diagnosis of Flat Feet and Bunions
Diagnosing flat feet and bunions involves several methods to accurately assess foot structure and function. A combination of physical examinations, imaging techniques, and gait analysis helps to identify these conditions.
Physical Examination
During a physical examination, a healthcare professional evaluates the foot’s shape and the position of the arches. The patient may be asked to stand and walk. The doctor looks for signs such as a bulging bump on the base of the big toe, swelling, and redness, which are indicators of bunions.
The examination may also include tests for flexibility and pain levels. Placing weight on the foot can reveal how flat feet affect alignment and pressure distribution. The symptoms often guide the doctor toward a diagnosis.
Imaging Techniques
If physical examination results are unclear, imaging techniques such as X-rays may be used. X-rays provide detailed images of the bone structure, helping to confirm the presence of bunions and assess their severity. They also help identify other foot deformities associated with flat feet.
In some cases, a CT scan or MRI may be recommended. These imaging methods give a comprehensive view of both the bones and surrounding soft tissues. This information is valuable for planning treatment options.
Gait Analysis
Gait analysis involves observing how a person walks. This analysis helps determine how flat feet and bunions impact overall movement. It can identify abnormal gait patterns that lead to further complications.
Foot pressure sensors may also be used during this analysis. They provide data on how weight is distributed across the foot. This information helps to identify stress points and can guide the choice of orthotics or footwear. Gait analysis is essential for developing a treatment plan tailored to the individual’s needs.
Treatment Strategies
Managing flat feet and bunions involves several effective strategies aimed at providing relief and preventing further issues.
Orthotic Inserts:
Custom or over-the-counter orthotic inserts can support the arches and help correct foot alignment. They relieve pressure on the bunion and improve comfort.
Footwear Choices:
Choosing the right shoes is essential. Footwear should have a wide toe box and flexible soles. Avoiding narrow or high-heeled shoes can reduce discomfort.
Exercises:
Regular foot and ankle exercises can strengthen the muscles. Stretching the arches and toes can help improve flexibility, which may alleviate pain.
Weight Management:
Maintaining a healthy weight can decrease the stress on the feet. Less weight can mean less pressure on bunions, leading to more comfort.
Ice and Pain Relief:
Applying ice to the affected area can reduce swelling. Over-the-counter pain medications can also help manage discomfort when needed.
Professional Help:
In some cases, consulting a podiatrist for custom orthotics or additional treatment options is beneficial. They can provide personalized advice based on specific needs.
Taking these steps can effectively manage the symptoms of flat feet and bunions, improving overall foot health. For more information, learn about bunion treatment options.
Conservative Treatment Options
Conservative treatment options for flat feet and bunions can help reduce discomfort and prevent further issues. These methods aim to manage symptoms without surgical intervention. Key approaches include orthotic devices, proper footwear recommendations, exercises, and medications.
Orthotic Devices
Orthotic devices are specially designed shoe inserts that provide support to the arches of the feet. These inserts can help redistribute pressure away from the bunion and improve foot alignment.
There are different types of orthotics available:
- Custom-made orthotics: Made specifically for the individual’s foot shape and needs.
- Over-the-counter options: Readily available and may provide moderate support.
Using orthotic devices regularly can alleviate pain and enhance mobility. They can be particularly beneficial for those with flat feet as they help to stabilize the foot’s structure.
Footwear Recommendations
Proper footwear plays a crucial role in managing flat feet and bunions. Shoes should offer ample room in the toe box and a supportive sole.
Key features to consider include:
- Arch support: Shoes with built-in arch support help maintain foot alignment.
- Wide toe box: Allows toes to move freely without pressure on the bunion.
- Flexible material: Promotes comfort and reduces irritation.
Wearing the right shoes can decrease pain and prevent bunions from worsening. People with flat feet should avoid high heels or overly tight footwear that limits movement.
Exercises and Physical Therapy
Exercises and physical therapy can strengthen the foot muscles and alleviate symptoms related to flat feet and bunions. Specific stretches and activities target foot and ankle flexibility.
Beneficial exercises include:
- Toe curls: Curling the toes to strengthen the foot muscles.
- Calf stretches: Improving flexibility and reducing tension in the calf area.
- Arch lifts: Strengthening the arches by lifting and lowering them.
Physical therapy can also include guided programs that focus on proper walking techniques. Regular exercise may improve overall foot function and reduce discomfort.
Medications and Pain Management
When conservative treatments are not enough, medications can help manage pain. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) reduce inflammation and relieve discomfort.
Over-the-counter options include:
- Ibuprofen
- Naproxen
In some cases, healthcare providers may recommend corticosteroid injections for more intense alleviation of swelling. While these medications can be effective, they should be used under medical supervision to avoid side effects.
Surgical Interventions
Surgical interventions can be important for those with flat feet and bunions, especially when conservative treatments fail. These surgeries aim to relieve pain and correct foot alignment issues, leading to improved mobility and quality of life.
Types of Surgery for Flat Feet
There are several types of surgeries designed to correct flat feet. One common procedure is the subtalar arthroereisis, which involves placing a small device in the subtalar joint to help support the arch. This option is often less invasive and allows for quicker recovery.
Another method is osteotomy, where a surgeon cuts and repositions the bones in the foot to create a more natural arch. This surgery can be more extensive and may involve longer recovery times but can provide significant relief from pain.
Joint fusion may also be necessary in severe cases. This involves fusing bones in the rearfoot to stabilize the joint, reducing pain and improving function. Each of these surgical options varies in complexity and recovery times, depending on the individual’s condition.
Surgical Procedures for Bunions
Bunion surgery, or bunionectomy, is typically recommended when non-surgical options do not alleviate pain effectively. The primary goal is to remove the bony growth and realign the big toe.
One common approach is the scarf osteotomy, where the surgeon reshapes the bone at an angle to reduce the bunion. This technique is effective for most bunion cases and allows for quicker recovery compared to traditional methods.
In some situations, an articular resurfacing may be required, which involves removing the damaged cartilage and reshaping the involved bones. This method requires careful assessment and can result in a more complex recovery.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovery from foot surgery varies based on the type of procedure performed. Generally, patients may need to wear a surgical boot or cast for several weeks to protect the area.
Physical therapy is often part of the rehabilitation process. Early therapy focuses on gentle range-of-motion exercises to prevent stiffness. As healing progresses, strengthening exercises will restore function and improve foot alignment.
Follow-up appointments are important to monitor healing and adjust rehabilitation as needed. Patients should be prepared for a gradual return to normal activities, which can take several months depending on the type of surgery and individual healing rates.
Preventing Flat Feet and Bunions
Taking steps toward prevention can significantly reduce the risk of flat feet and bunions. Lifestyle choices and proper footwear play crucial roles in maintaining healthy feet and reducing discomfort.
Lifestyle Modifications
Certain lifestyle changes can greatly impact foot health. Maintaining a healthy weight is key because excess weight puts additional stress on the feet, increasing the risk of flat feet.
Engaging in regular physical activity helps strengthen muscles in the feet and legs. Stretching exercises can improve flexibility and support proper foot alignment.
Incorporating activities like yoga or Pilates can enhance balance and strengthen stabilizing muscles. Avoiding activities that involve excessive pressure on the feet, like prolonged standing or high-impact sports, is also important.
In addition, practicing good foot hygiene can prevent conditions that may lead to bunions. Keeping feet clean and dry reduces the risk of skin infections and complications.
Importance of Proper Footwear
Choosing the right shoes is essential for foot health. Shoes that have a wide toe box allow the toes to move freely, reducing the risk of bunions.
Footwear should provide proper arch support, helping to maintain natural foot alignment. Non-slip soles can enhance stability and prevent slips and falls.
It is important to avoid narrow or high-heeled shoes, as they can worsen foot problems. Custom orthotics or over-the-counter inserts can also support and correct foot position.
Regularly measuring foot size ensures the right fit, as feet can change over time. Wearing well-fitted shoes will help protect against discomfort and long-term issues such as flat feet and bunions.
Considerations for Special Populations
Certain populations face unique challenges concerning flat feet and bunions. Understanding these challenges helps in providing effective care and management for each group.
Children and Adolescents
Flat feet can develop during childhood and often require careful monitoring. Many children are born with flexible flat feet, which may improve as they grow. However, persistent flat feet can lead to discomfort and other issues.
Parents should be aware of signs such as foot pain, difficulty running, or changes in walking patterns. Early intervention may include custom orthotics or supportive footwear. In some cases, physical therapy can strengthen foot muscles and improve alignment.
Regular check-ups with a podiatrist can help in assessing foot development and ensuring that any potential issues are addressed in a timely manner.
Athletes
Athletes, especially runners, may experience increased strain on their feet due to flat feet and a higher risk of developing bunions. Their training regimens can exacerbate foot pain and complications.
Choosing appropriate footwear is essential. Supportive shoes with proper arch support can help mitigate some issues. In some cases, custom orthotics designed for athletic activity can offer added support and stability.
Injuries may also be more common among athletes with flat feet. It’s crucial for them to warm up properly and pay attention to any signs of pain. Seeking advice from a sports medicine specialist can ensure proper training techniques and foot care.
Elderly Patients
Elderly individuals often experience foot problems due to age-related changes. Flat feet can lead to discomfort, balance issues, and an increased risk of falls.
Bunions can also become problematic, as they may cause pain and difficulty in finding comfortable shoes. Regular foot examinations become necessary to detect any changes.
Footwear is crucial for elderly patients. They should choose shoes that provide ample room in the toe box and proper arch support. Stretching exercises can improve flexibility and strength, reducing discomfort. In some cases, surgical options may be considered if conservative treatments fail to provide relief.
Advancements in Treatment and Research
Recent advancements in the treatment of flat feet and bunions focus on both non-surgical and surgical options.
Non-Surgical Treatments:
- Orthotic Devices: Custom insoles help to support the arches and reduce pain.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises strengthen foot muscles and improve flexibility.
Surgical Innovations:
- Minimally Invasive Techniques: New methods, such as minimally invasive bunion surgery (MIBS), reduce recovery time and tissue damage.
- Improved Surgical Methods: Surgeons are exploring various techniques to correct bunions with less complications.
Clinical trials are crucial for discovering effective treatments. Researchers are investigating the long-term effects of different procedures. This aims to minimize recurrence rates in bunion surgery.
Additionally, studies are evaluating the role of footwear in preventing these conditions. Proper shoe design can significantly impact foot health.
The future of bunion and flat feet treatment lies in personalized medicine. Tailoring approaches to individual anatomy will likely lead to better outcomes.
New findings continue to emerge, providing hope for improved treatment options in the coming years. As research progresses, there is a growing understanding of how to manage these conditions effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
Many individuals dealing with flat feet and bunions have specific queries about managing their conditions. The following questions address common concerns related to exercises, footwear choices, causes of bunions, and activities to avoid.
What exercises can help alleviate symptoms associated with flat feet and bunions?
Exercises that strengthen the foot and improve flexibility can be beneficial. Stretching the calf muscles and using resistance bands to strengthen the arch can help. Foot rolls using a ball can also relieve tension and increase mobility.
Is it possible to reduce the size of bunions without surgical intervention?
While bunions typically do not shrink, non-surgical options can help manage pain and discomfort. Using orthotic devices or pads may help relieve pressure. Some people find relief through bracing or specific exercises that encourage better alignment.
What type of footwear is recommended for those suffering from flat feet and bunions?
Footwear that provides ample support is crucial. Shoes with a wide toe box and good arch support are recommended. Avoiding high heels and narrow shoes can help prevent worsening of the condition.
Bunions are often caused by genetic factors, improper footwear, and foot structure. Flat feet can contribute to the development of bunions through misalignment of the big toe joint. This misalignment creates added stress, leading to painful bony growths.
Are certain foot shapes more susceptible to developing bunions?
Yes, individuals with flat feet, high arches, or those with a specific foot shape may be more prone to bunions. These shapes can lead to an imbalance in weight distribution, increasing pressure on the big toe joint.
What activities or habits should individuals with flat feet avoid to prevent exacerbating their condition?
Individuals with flat feet should avoid prolonged standing or walking on hard surfaces. High-impact activities might also worsen their symptoms. It is advisable to take breaks and choose lower-impact exercises to prevent further strain on the feet.







